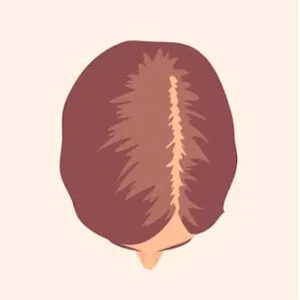
Female pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is a common condition that affects millions of women worldwide. It can have a profound impact on self-esteem and quality of life, making it essential to understand its progression and classification. The Ludwig Scale is a valuable tool that helps in categorizing and assessing the severity of female pattern baldness. In this article, we’ll delve into the Ludwig Scale and how it plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis and treatment of this condition.
The Ludwig Scale: A Grading System for Female Pattern Baldness
The Ludwig Scale, developed by Dr. E. Ludwig in 1977, is a standardized method for classifying the progression of female pattern baldness. It divides the condition into three distinct stages, each with varying degrees of severity. By using this scale, medical professionals can assess the extent of hair loss, enabling them to recommend appropriate treatments. Let’s take a closer look at the three stages of the Ludwig Scale:
Ludwig Stage I: Minimal Thinning
In this stage, the hair loss is mild and primarily involves thinning of the hair around the crown of the head.
The hairline remains largely intact, and the part may appear wider than usual.
Many women in this stage may not even realize they are experiencing hair loss, attributing it to natural aging.
Ludwig Stage III: Extensive Thinning
Stage III represents advanced hair loss, with significant thinning and recession of the hairline.
The part becomes considerably wider, and scalp visibility is more pronounced.
At this point, women often seek professional assistance for hair restoration.
The Importance of the Ludwig Scale
The Ludwig Scale serves several critical functions in the context of female pattern baldness:
Accurate Diagnosis: By categorizing the severity of hair loss, the Ludwig Scale allows healthcare providers to make precise diagnoses and recommend appropriate treatments.
Monitoring Progression: This scale enables healthcare professionals to track the progression of female pattern baldness over time, helping to determine the effectiveness of treatments.
Treatment Planning: Different stages of the Ludwig Scale may require varying treatment approaches. Knowing the stage of hair loss is essential for tailoring treatment plans to the individual needs of each patient.
Emotional Support: Understanding the stage of hair loss can help women anticipate and address the emotional and psychological impact of female pattern baldness. It may also motivate them to seek treatment earlier.
The Ludwig Scale is an invaluable tool for classifying female pattern baldness, helping healthcare providers determine the severity of the condition and tailor treatment plans accordingly. By understanding the stages of hair loss, women can take proactive steps to address their concerns and seek appropriate treatment. If you are experiencing female pattern baldness, consult with a healthcare professional to explore suitable treatment options and regain confidence in your appearance.
Thanks to Dr. Okan TANIN, the first name that comes to mind when it comes to hair transplantation in Antalya, and his experienced team, you will find a solution to your problem. Hair transplantation in Turkey is now a very popular option all over the world. In fact, be sure to check out the hair transplantation and holiday combination packages, especially in Antalya. Don’t be late and confront your hair loss immediately and evaluate treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions of Female Pattern Baldness
Female Pattern Baldness (FPB), also known as androgenetic alopecia in women, is a type of hair loss that affects women, typically characterized by thinning hair or a widening part. It’s often genetically inherited and can be influenced by hormonal changes.
The Ludwig Scale is a method used to classify the severity and pattern of hair loss in women. It ranges from Stage I (mild) to Stage III (severe), helping to standardize the assessment of female hair loss and assist in treatment planning.
While both conditions are forms of androgenetic alopecia and can be hereditary, the pattern of hair loss differs. In men, it often starts with a receding hairline and progresses to baldness at the top of the head. In women, it usually begins with a widening part and general thinning without a receding hairline.
Treatment options are available but depend on the severity and underlying causes. Minoxidil (Rogaine) is often recommended and can be effective in slowing hair loss and promoting regrowth. Other treatments include hormone therapy, laser therapy, or hair transplant surgery. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for a personalized treatment plan.
Since it’s often genetically inherited, it’s difficult to prevent. However, maintaining a healthy diet, reducing stress, and avoiding harsh hair treatments can help in managing the condition. Early detection and treatment can also mitigate the severity of hair loss.
Call Us Today for FREE Consultations
ASK A QUESTION